私達の認知は価値判断とともにあり、価値は外界の情報や内部状態をもとに自動的に決まってきます。この価値判断を行う神経回路は大脳皮質の眼窩前頭前野、大脳基底核の側坐核、視床の背内側核が作る辺縁系ループ回路がメインとなっていると考えられています。この神経回路に対して外界の情報や内部状態の快不快についての情報を提供するのが扁桃体で、扁桃体や側坐核に対して価値そのものの情報*1を送るのが腹側被蓋野を含むドーパミン神経(A10*2)であると考えられてきました。既にいろいろな名前が出てきてややこしくなっていますが、辺縁系ループ回路、扁桃体、A10神経は相互接続によって状況や行動の価値を定めていると想像されます(下図)。
Our cognition works with value estimation, and the value is automatically determined by the outside information and internal state. The neuronal circuitry responsible for the value estimation is mainly composed by the limbic loop system formed by orbitofrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and mediodorsal thalamic nucleus. Amygdala provides outside information and internal pleasant/unpleasant condition to the loop, and A10 dopamine system including ventral tegmental area provides value information to amygdala and nucleus accumbens. In general, limbic loop, amygdala, and A10 interlink to gether and are considered to code values of condition and behaviors.
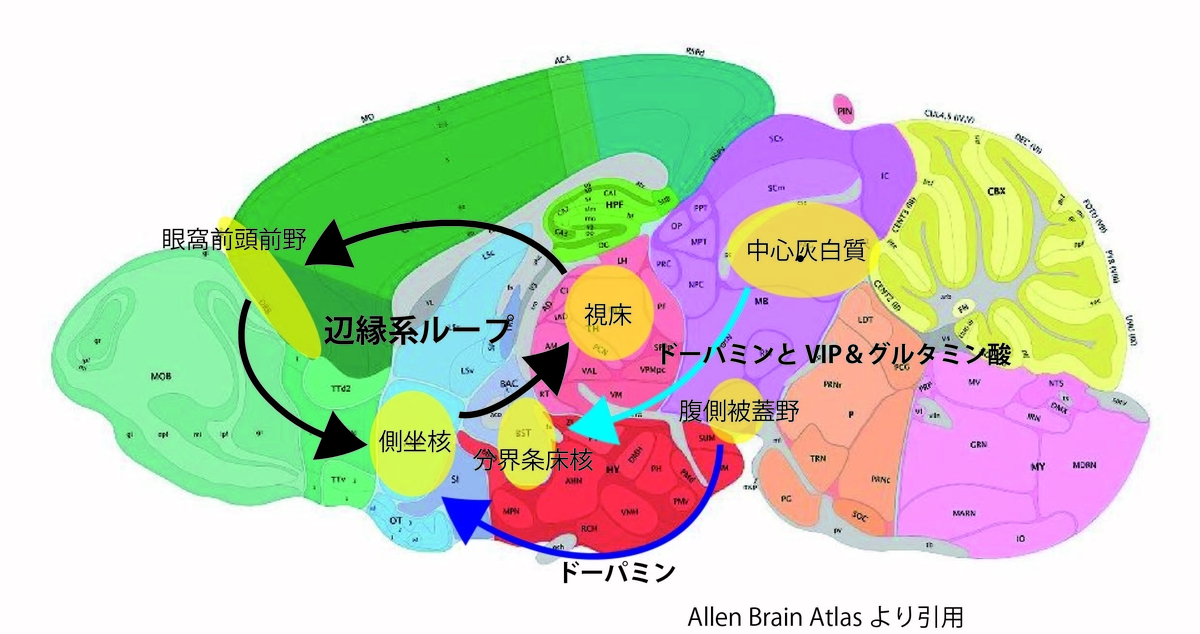 このような大枠はわかっているものの、この回路を構成するそれぞれの脳領域が様々な機能ドメインに細分化されていることが近年の研究によってわかってきました。今回の研究で注目したのが扁桃体中心核と分界条床核という拡張扁桃体と総称される脳領域に対して入力するA10神経細胞です。これら拡張扁桃体は嫌悪、不安、恐怖といった情動行動の発現に関与しており、この領域へのドーパミン神経の入力は極めて重要です。A10神経といえば腹側被蓋野、と多くの人が考えており、扁桃体中心核や分界条床核へのドーパミン入力も腹側被蓋野に由来する、と考えられてきました。しかしながら、ドーパミン含有神経は腹側被蓋野以外にも広がっており、近年拡張扁桃体へのドーパミン神経は腹側被蓋野より後方の背側縫線核や中心灰白質に由来することが報告されていました。一方、これら背側縫線核や中心灰白質にはドーパミン神経以外にも様々なニューロンが入り混じっており、拡張扁桃体へのドーパミン作用の神経回路を考える上でこれらの領域のニューロンの分類が必要な状態でした。
このような大枠はわかっているものの、この回路を構成するそれぞれの脳領域が様々な機能ドメインに細分化されていることが近年の研究によってわかってきました。今回の研究で注目したのが扁桃体中心核と分界条床核という拡張扁桃体と総称される脳領域に対して入力するA10神経細胞です。これら拡張扁桃体は嫌悪、不安、恐怖といった情動行動の発現に関与しており、この領域へのドーパミン神経の入力は極めて重要です。A10神経といえば腹側被蓋野、と多くの人が考えており、扁桃体中心核や分界条床核へのドーパミン入力も腹側被蓋野に由来する、と考えられてきました。しかしながら、ドーパミン含有神経は腹側被蓋野以外にも広がっており、近年拡張扁桃体へのドーパミン神経は腹側被蓋野より後方の背側縫線核や中心灰白質に由来することが報告されていました。一方、これら背側縫線核や中心灰白質にはドーパミン神経以外にも様々なニューロンが入り混じっており、拡張扁桃体へのドーパミン作用の神経回路を考える上でこれらの領域のニューロンの分類が必要な状態でした。
Although the basic circuitry is known, recent studies have shown that the real circuitry is more complicated as each of the components is found to be organized into various functional domains. In the current study we focused on A10 dopaminergic fibers targetting the extended amygdala composed of the central nucleus of the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. The extended amygdala is related with emotional expression such as aversion, anxiety, and fear, and dopaminergic input to the area is especially important. Many people regard ventral tegmental area as A10 and dopaminergic input to the extended amygdala was thought to be originated from the ventral tegmental area. However, dopaminergic neurons extend out from the ventral tegmental area, and recent studies have shown that dopaminergic input to the extended amygdala originates from dorsal raphe and periaqueductal gray (DR-PAG). On the other hand, the DR-PAG are heterogenious structure and consisted of various cell types in addition to dopaminergic neurons, and characterization of cell types in the area is needed for considering action of dopanine on the extended amygdala.
今回の研究で、私たちは遺伝子組換えマウス、ウイルスベクター、免疫組織化学、遺伝子組織化学(in situ hybridization)、神経路追跡法を組み合わせることで、拡張扁桃体へ出力する背側縫線核や中心灰白質の細胞の分類を試みました。
In this study, we combined transgenic mice, viral vectors, immunohistochemistry, in situ hybridization, and tract tracing methods to classify cell types in the dorsal raphe and periaqueductal gray neurons which project to the extended amygdala.
すると、拡張扁桃体へ出力する背側縫線核や中心灰白質の細胞でドーパミン神経であると判定できた細胞は4割ほどであること、行動の性差に関与するVIPという神経ペプチドを発現するニューロンの殆どはドーパミンを持たず、多くが興奮性神経伝達物質であるグルタミン酸を放出する細胞であることが明らかとなりました(図 水色矢印)。このように、背側縫線核や中心灰白質から拡張扁桃体への出力は多様であり、今後の研究はこの多様性を考慮することが重要であるといえます。また、この領域のドーパミン神経が本当に腹側被蓋野のドーパミン神経と同様の作用を有するか、ということも検討しなければならないでしょう。
As the result, we found that dopaminergic neurons consisted of about 40% of DR-PAG neurons projecting to the extended amygdala, VIP neurons, related to sexual dimorphic behaviors, rarely express dopamine but release glutamate, the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. Thus, output from DR-PAG to the extended amygdala is heterogenious, and future studies should take account for the variety. It is also needed to address whether the dopamine fibers in the area have similar funtions of those in ventral tegmental area.
また、ドーパミン神経の信頼できるマーカーとして、ドーパミン合成にかかわるチロシン水酸化酵素(tyrosine hydroxylase, TH)があり、その他、細胞間隙に放出されたドーパミンを回収するドーパミン輸送体(dopamine transporter, DAT)が有名です。ところが、今回THとDATの発現はそれほど重なっていないことがわかり、DATのトランスジェニックマウスはドーパミン神経の研究に用いる際は注意が必要であることが示唆されます。
In addition, the common markers for dopaminergic neurons are tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), which is responsible for the production of dopamine, and dopamine transporter (DAT), which collects extracellular dopamine. However, we also found that overlap of TH and DAT is restricted. This result implies that care must be taken to interpret data from DAT transgenic mice for dopaminergic neurons.
今回の研究は、金沢医科大学の山本亮博士を中心としたグループによって行われ、本研究室からは伊藤と相古が関与しています。筆者(伊藤)は研究の開始時から関与しており、筆頭著者が苦労しているさまを間近で見てきました。最終的にしっかりとした研究にまとまり、そこに重要な貢献ができたことを嬉しく思います。
The current study is mainly done by a group of Kanazawa Medical University led by Dr. Ryo Yamamoto, and from our laboratory, Ito and Soko participated in the study. The writer (Ito) took a part of the study from the begininng, and had seen that the first author did hard work. Finally the work took a shape, and the writer is pleased to make important contribution.